Databases: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) (→ACID) |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOINDEX__ | |||
[[file:Database.png|right|frame|Databases<ref>http://www.flaticon.com/</ref>]] | [[file:Database.png|right|frame|Databases<ref>http://www.flaticon.com/</ref>]] | ||
A database is an organized collection of data. It is the collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views and other objects. The data are typically organized to model aspects of reality in a way that supports processes requiring information, such as modelling the availability of rooms in hotels in a way that supports finding a hotel with vacancies.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Database</ref> | A database is an organized collection of data. It is the collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views and other objects. The data are typically organized to model aspects of reality in a way that supports processes requiring information, such as modelling the availability of rooms in hotels in a way that supports finding a hotel with vacancies.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Database</ref> | ||
== Big Ideas in Databases == | == Big Ideas in Databases == | ||
== | * [[Entity relationship diagramming]] | ||
* [[Normalization]] | |||
== ACID == | |||
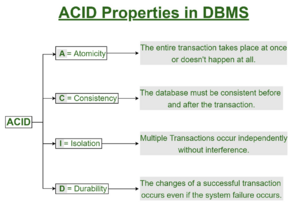
In computer science, ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a transaction. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ACID</ref> | |||
[[File:Acid.png|thumb]] | |||
== | == See also == | ||
# Please take a look at our [[SQL]] page | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 08:03, 1 September 2022

A database is an organized collection of data. It is the collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views and other objects. The data are typically organized to model aspects of reality in a way that supports processes requiring information, such as modelling the availability of rooms in hotels in a way that supports finding a hotel with vacancies.[2]
Big Ideas in Databases[edit]
ACID[edit]
In computer science, ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a transaction. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction.[3]
See also[edit]
- Please take a look at our SQL page