Candidate block: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
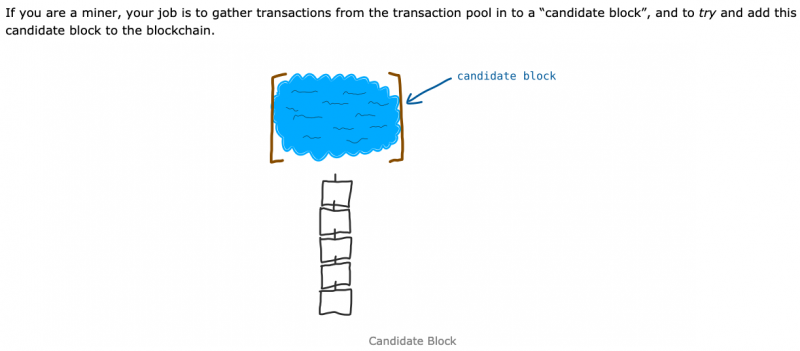
Candidate blocks are blocks created by miners as part of a proof-of-work consensus process. A miner will receive a block reward when it produces a candidate block with a valid block hash and broadcasts this block to the network's nodes, who verify the hash's authenticity. In this manner, every (non-genesis) block on a blockchain begins its life as one of many pre-validated candidate blocks.<ref>https://sci.smithandcrown.com/glossary/candidate-block</ref> | Candidate blocks are blocks created by miners as part of a proof-of-work consensus process. A miner will receive a block reward when it produces a candidate block with a valid block hash and broadcasts this block to the network's nodes, who verify the hash's authenticity. In this manner, every (non-genesis) block on a blockchain begins its life as one of many pre-validated candidate blocks.<ref>https://sci.smithandcrown.com/glossary/candidate-block</ref> | ||
[[File:Candidate block.png|800px]]<ref>https://learnmeabitcoin.com/beginners/blocks</ref> | |||
A candidate block is a temporary block created using transactions selected from the memory pool.<ref>https://learnmeabitcoin.com/guide/candidate-block</ref> | A candidate block is a temporary block created using transactions selected from the memory pool.<ref>https://learnmeabitcoin.com/guide/candidate-block</ref> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 10:13, 7 March 2020
Advanced Programming[1]
Candidate blocks are blocks created by miners as part of a proof-of-work consensus process. A miner will receive a block reward when it produces a candidate block with a valid block hash and broadcasts this block to the network's nodes, who verify the hash's authenticity. In this manner, every (non-genesis) block on a blockchain begins its life as one of many pre-validated candidate blocks.[2]
A candidate block is a temporary block created using transactions selected from the memory pool.[4]