Procedural thinking: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Procedural thinking is a disciplined method of thinking in sequence, in order and logically. Procedural thinking can be reflected in a flow chart. Some examples below | Procedural thinking is a disciplined method of thinking in sequence, in order and logically. Procedural thinking can be reflected in a flow chart. Some examples below may help you better understand procedural thinking: | ||
# Following a recipe requires procedural thinking because you must follow the steps in order | |||
# Putting together Ikea furniture requires procedural thinking because you usually follow the steps in order | |||
# Procedural thinking is used when performing CPR to save someone's life - you follow a series of steps (call for help, check breathing, check airway, check circulation, decide if you perform CPR) | |||
# When you print something on a school printer, you follow a series of sequential steps (choose what to print, click print, choose a printer, go to the printer, and then scan your barcode). | |||
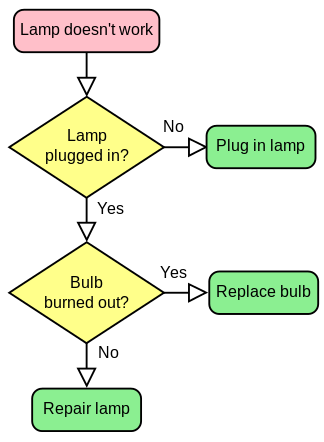
# If a lamp is broken, you might follow these steps in the flowchart below<ref>By svg by Booyabazookaoriginal png by Wapcaplet - vector version of Image:LampFlowchart.png, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=714537</ref>: | |||
[[File:LampFlowchart.png]] | |||
== Standards == | == Standards == | ||
These standards are used from the IB Computer Science Subject Guide<ref>IB Diploma Programme Computer science guide (first examinations 2014). Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom: International Baccalaureate Organization. January 2012.</ref> | |||
* Identify the procedure appropriate to solving a problem. | * Identify the procedure appropriate to solving a problem. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 20:39, 17 November 2022

Procedural thinking[1]
Procedural thinking is a disciplined method of thinking in sequence, in order and logically. Procedural thinking can be reflected in a flow chart. Some examples below may help you better understand procedural thinking:
- Following a recipe requires procedural thinking because you must follow the steps in order
- Putting together Ikea furniture requires procedural thinking because you usually follow the steps in order
- Procedural thinking is used when performing CPR to save someone's life - you follow a series of steps (call for help, check breathing, check airway, check circulation, decide if you perform CPR)
- When you print something on a school printer, you follow a series of sequential steps (choose what to print, click print, choose a printer, go to the printer, and then scan your barcode).
- If a lamp is broken, you might follow these steps in the flowchart below[2]:
Standards[edit]
These standards are used from the IB Computer Science Subject Guide[3]
- Identify the procedure appropriate to solving a problem.
References[edit]
- ↑ http://www.flaticon.com/
- ↑ By svg by Booyabazookaoriginal png by Wapcaplet - vector version of Image:LampFlowchart.png, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=714537
- ↑ IB Diploma Programme Computer science guide (first examinations 2014). Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom: International Baccalaureate Organization. January 2012.