Operators: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[file:arrows.png|right|frame|Programming basics<ref>http://www.flaticon.com/</ref>]] | [[file:arrows.png|right|frame|Programming basics<ref>http://www.flaticon.com/</ref>]] | ||
An operator is | An operator is symbol that takes one or more values (or expressions, in programming jargon) and yields another value (so that the construction itself becomes an expression)<ref>http://php.net/manual/en/language.operators.php</ref>. | ||
There are many different types of operators, but the ones we primarily concern ourselves with are boldfaced below: | There are many different types of operators, but the ones we primarily concern ourselves with are boldfaced below. If you'd like to learn more about different types of operators in PHP, [http://php.net/manual/en/language.operators.php please click here]. | ||
* Operator Precedence | * Operator Precedence | ||
* '''Arithmetic Operators''' | * '''Arithmetic Operators''' | ||
* Assignment Operators | * '''Assignment Operators''' | ||
* Bitwise Operators | * Bitwise Operators | ||
* '''Comparison Operators''' | * '''Comparison Operators''' | ||
| Line 28: | Line 22: | ||
== Assignment operators == | |||
An example of some '''arithmetic''' operators in PHP can be found below: | An assignment operator assigns a value to its left operand based on the value of its right operand.<ref>https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Assignment_Operators</ref> | ||
== Arithmetic operators == | |||
Arithmetic operators take numerical values (either literals or variables) as their operands and return a single numerical value. The standard arithmetic operators are addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), and division (/).<ref>https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Arithmetic_Operators</ref> | |||
An example of some '''arithmetic''' operators in PHP can be found below <ref>http://php.net/manual/en/language.operators.arithmetic.php</ref>. | |||
{| style="width: 95%;" class="wikitable" | {| style="width: 95%;" class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 50: | Line 51: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| $a ** $b ||Exponentiation|| Result of raising $a to the $b'th power. | | $a ** $b ||Exponentiation|| Result of raising $a to the $b'th power. | ||
|} | |||
An example of some '''arithmetic''' operators in Python can be found below <ref>https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/basic-operators-python/</ref>. | |||
{| style="width: 95%;" class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
!Example !! Name !! Result | |||
|- | |||
| a + b ||Addition|| Sum of a and b. | |||
|- | |||
| a - b|| Subtraction ||Difference of a and b. | |||
|- | |||
| a * b||Multiplication|| Product of a and b. | |||
|- | |||
| a / b|| Division|| Quotient of a and b. | |||
|- | |||
| a % b||Modulus|| Remainder of a divided by b. | |||
|- | |||
| a ** b ||Exponentiation|| Result of raising a to the b'th power. | |||
|} | |||
== Comparison operators == | |||
Comparison operators, as their name implies, allow you to compare two values.<ref>https://www.php.net/manual/en/language.operators.comparison.php</ref> | |||
An example of some '''conditional''' operators in PHP can be found below <ref>http://php.net/manual/en/language.operators.comparison.php</ref>. | |||
{| style="width: 95%;" class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
!Example !! Name !! Result | |||
|- | |||
|$a == $b ||Equal ||TRUE if $a is equal to $b after [http://php.net/manual/en/language.types.type-juggling.php type juggling.] | |||
|- | |||
|$a === $b|| Identical ||TRUE if $a is equal to $b, and they are of the same type. | |||
|- | |||
|$a != $b|| Not equal|| TRUE if $a is not equal to $b after [http://php.net/manual/en/language.types.type-juggling.php type juggling.]. | |||
|- | |||
|$a <> $b|| Not equal|| TRUE if $a is not equal to $b after [http://php.net/manual/en/language.types.type-juggling.php type juggling.] | |||
|- | |||
|$a !== $b ||Not identical ||TRUE if $a is not equal to $b, or they are not of the same type. | |||
|- | |||
|$a < $b ||Less than ||TRUE if $a is strictly less than $b. | |||
|- | |||
|$a > $b ||Greater than|| TRUE if $a is strictly greater than $b. | |||
|- | |||
|$a <= $b ||Less than or equal to|| TRUE if $a is less than or equal to $b. | |||
|- | |||
|$a >= $b ||Greater than or equal to|| TRUE if $a is greater than or equal to $b. | |||
|- | |||
|$a <=> $b ||Spaceship ||An integer less than, equal to, or greater than zero when $a is respectively less than, equal to, or greater than $b. Available as of PHP 7. | |||
|} | |||
An example of some '''conditional''' operators in Python can be found below <ref>https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/basic-operators-python/</ref>. | |||
{| style="width: 95%;" class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
!Example !! Name !! Result | |||
|- | |||
|a == b ||Equal ||TRUE if a is equal to b | |||
|- | |||
|a != b|| Not equal|| TRUE if a is not equal to b | |||
|- | |||
|a < b ||Less than ||TRUE if a is strictly less than b. | |||
|- | |||
|a > b ||Greater than|| TRUE if a is strictly greater than b. | |||
|- | |||
|a <= b ||Less than or equal to|| TRUE if a is less than or equal to b. | |||
|- | |||
|a >= b ||Greater than or equal to|| TRUE if a is greater than or equal to b. | |||
|- | |||
| a in b || in || TRUE if a is in b. | |||
|- | |||
| a not in b || not in || TRUE if a is NOT in b | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 61: | Line 139: | ||
== The way the IB wants you to use operators == | == The way the IB wants you to use operators == | ||
Please know all code submitted to the IB (with the exception of object oriented programming) is in [[pseudocode]]. The way we write operators in [[pseudocode]] is different than the way we might write them in the real world. | Please know all code submitted to the IB (with the exception of object oriented programming option) is in [[pseudocode]]. The way we write operators in [[pseudocode]] is different than the way we might write them in the real world. | ||
[[:media:Approved notation for developing pseudocode.pdf | Click here to view a file describing approved notation, including pseudocode This is the approved notation sheet from the IB.]] | [[:media:Approved notation for developing pseudocode.pdf | Click here to view a file describing approved notation, including pseudocode This is the approved notation sheet from the IB.]] | ||
| Line 68: | Line 146: | ||
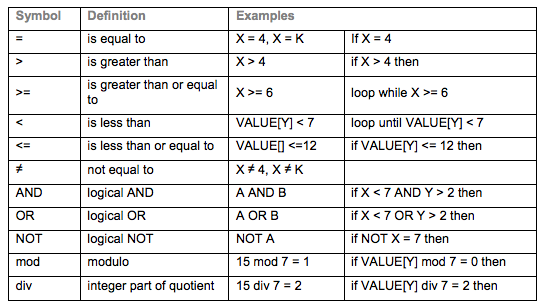
[[File:Ib operators.png]] | [[File:Ib operators.png]] | ||
== Python operators cheatsheet == | |||
[[:File:Python3 reference cheat sheet.pdf|Click here for an excellent python cheatsheet]] | |||
== Standards == | == Standards == | ||
| Line 74: | Line 156: | ||
* Define common operators. | * Define common operators. | ||
* Analyse the use of variables, constants and operators in algorithms. | * Analyse the use of variables, constants and operators in algorithms. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 16:05, 2 September 2023

An operator is symbol that takes one or more values (or expressions, in programming jargon) and yields another value (so that the construction itself becomes an expression)[2].
There are many different types of operators, but the ones we primarily concern ourselves with are boldfaced below. If you'd like to learn more about different types of operators in PHP, please click here.
- Operator Precedence
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Error Control Operators
- Execution Operators
- Incrementing/Decrementing Operators
- Logical Operators
- String Operators
- Array Operators
- Type Operators
Assignment operators[edit]
An assignment operator assigns a value to its left operand based on the value of its right operand.[3]
Arithmetic operators[edit]
Arithmetic operators take numerical values (either literals or variables) as their operands and return a single numerical value. The standard arithmetic operators are addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), and division (/).[4]
An example of some arithmetic operators in PHP can be found below [5].
| Example | Name | Result |
|---|---|---|
| +$a | Identity | Conversion of $a to int or float as appropriate. |
| -$a | Negation | Opposite of $a. |
| $a + $b | Addition | Sum of $a and $b. |
| $a - $b | Subtraction | Difference of $a and $b. |
| $a * $b | Multiplication | Product of $a and $b. |
| $a / $b | Division | Quotient of $a and $b. |
| $a % $b | Modulus | Remainder of $a divided by $b. |
| $a ** $b | Exponentiation | Result of raising $a to the $b'th power. |
An example of some arithmetic operators in Python can be found below [6].
| Example | Name | Result |
|---|---|---|
| a + b | Addition | Sum of a and b. |
| a - b | Subtraction | Difference of a and b. |
| a * b | Multiplication | Product of a and b. |
| a / b | Division | Quotient of a and b. |
| a % b | Modulus | Remainder of a divided by b. |
| a ** b | Exponentiation | Result of raising a to the b'th power. |
Comparison operators[edit]
Comparison operators, as their name implies, allow you to compare two values.[7]
An example of some conditional operators in PHP can be found below [8].
| Example | Name | Result |
|---|---|---|
| $a == $b | Equal | TRUE if $a is equal to $b after type juggling. |
| $a === $b | Identical | TRUE if $a is equal to $b, and they are of the same type. |
| $a != $b | Not equal | TRUE if $a is not equal to $b after type juggling.. |
| $a <> $b | Not equal | TRUE if $a is not equal to $b after type juggling. |
| $a !== $b | Not identical | TRUE if $a is not equal to $b, or they are not of the same type. |
| $a < $b | Less than | TRUE if $a is strictly less than $b. |
| $a > $b | Greater than | TRUE if $a is strictly greater than $b. |
| $a <= $b | Less than or equal to | TRUE if $a is less than or equal to $b. |
| $a >= $b | Greater than or equal to | TRUE if $a is greater than or equal to $b. |
| $a <=> $b | Spaceship | An integer less than, equal to, or greater than zero when $a is respectively less than, equal to, or greater than $b. Available as of PHP 7. |
An example of some conditional operators in Python can be found below [9].
| Example | Name | Result |
|---|---|---|
| a == b | Equal | TRUE if a is equal to b |
| a != b | Not equal | TRUE if a is not equal to b |
| a < b | Less than | TRUE if a is strictly less than b. |
| a > b | Greater than | TRUE if a is strictly greater than b. |
| a <= b | Less than or equal to | TRUE if a is less than or equal to b. |
| a >= b | Greater than or equal to | TRUE if a is greater than or equal to b. |
| a in b | in | TRUE if a is in b. |
| a not in b | not in | TRUE if a is NOT in b |
A video[edit]
This video references the C programming language and scratch, but the ideas about operators are excellent. In the case of conditionals, PHP and C share similar syntax (but not exact).
The way the IB wants you to use operators[edit]
Please know all code submitted to the IB (with the exception of object oriented programming option) is in pseudocode. The way we write operators in pseudocode is different than the way we might write them in the real world.
Below is a graphic that is taken from the above PDF file to help you understand how the IB wants operators to look.
Python operators cheatsheet[edit]
Click here for an excellent python cheatsheet
Standards[edit]
- Define the terms: variable, constant, operator, object.
- Define common operators.
- Analyse the use of variables, constants and operators in algorithms.
References[edit]
- ↑ http://www.flaticon.com/
- ↑ http://php.net/manual/en/language.operators.php
- ↑ https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Assignment_Operators
- ↑ https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Arithmetic_Operators
- ↑ http://php.net/manual/en/language.operators.arithmetic.php
- ↑ https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/basic-operators-python/
- ↑ https://www.php.net/manual/en/language.operators.comparison.php
- ↑ http://php.net/manual/en/language.operators.comparison.php
- ↑ https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/basic-operators-python/