Concurrency: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Concurrence is simultaneous occurrence. We could say something is '''concurrent''' when two processes happen at the same time. | Concurrence is simultaneous occurrence. We could say something is '''concurrent''' when two processes happen at the same time. | ||
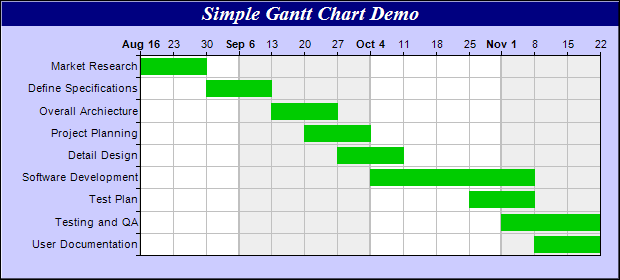
Below, you can see '''classic example of concurrency''' in a gantt chart. | Below, you can see '''classic example of concurrency''' in a gantt chart, which is used to plan a project. | ||
A note of caution. There are two different ways of looking at concurrency: | |||
# Concurrency can be used in project management and software development where multiple tasks are implemented at the same time. See the Gantt chart below for an example. | |||
# Concurrency can also be used in software in concurrent processing. We could also call this asynchronous programming. In this sense, we program to take advantage of inactive CPU processing time. Rather than process one task, wait, and then process another another task, we can process a second task as we are waiting for the first task to complete. | |||
== Example == | == Example == | ||
[[File:Gantt chart.png]] | |||
Revision as of 14:46, 25 July 2017

Exceptions[1]
Concurrence is simultaneous occurrence. We could say something is concurrent when two processes happen at the same time. Below, you can see classic example of concurrency in a gantt chart, which is used to plan a project.
A note of caution. There are two different ways of looking at concurrency:
- Concurrency can be used in project management and software development where multiple tasks are implemented at the same time. See the Gantt chart below for an example.
- Concurrency can also be used in software in concurrent processing. We could also call this asynchronous programming. In this sense, we program to take advantage of inactive CPU processing time. Rather than process one task, wait, and then process another another task, we can process a second task as we are waiting for the first task to complete.
Example[edit]
Do you understand this?[edit]
Standards[edit]
These standards are used from the IB Computer Science Subject Guide[2]
- Identify the parts of a solution that could be implemented concurrently
- Describe how concurrent processing can be used to solve a problem
- Evaluate the decision to use concurrent processing in solving a problem
References[edit]
- ↑ http://www.flaticon.com/
- ↑ IB Diploma Programme Computer science guide (first examinations 2014). Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom: International Baccalaureate Organization. January 2012.