Computer resources: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| Network connectivity || foo | | Network connectivity || foo | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Tools you can use to manage different parts of the Linux operating system == | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! The OS manages !! Linux tools you can use to understand what is going on | |||
|- | |||
| Memory || top, htop, free, vmstat | |||
|- | |||
| Processes || top | |||
|- | |||
| Files || File system, df, du, mount, lsof | |||
|- | |||
| Security || fstab, last, who, /var/log/auth.log | |||
|- | |||
| CPU Scheduling || perf | |||
|- | |||
| Devices, Device I/O|| iotop, iostat | |||
|- | |||
| Interrupts || perf | |||
|- | |||
| Networks || netstat, top, tcpdump, iptraf, iftop, nmon | |||
|} | |||
[[Media:Linux observability tools.png | Click here for a brilliant graphic showing the different types of tools you can use to view inside the Linux operating system]] | |||
== an excellent video to get you started == | == an excellent video to get you started == | ||
Revision as of 12:10, 29 November 2017

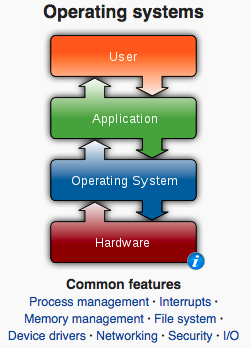
Resource Management[1]
A system resource is any usable part of a computer that can be controlled and assigned by the operating system so all of the hardware and software on the computer can work together as designed. System resources can be used by users, like you, when you open programs and apps, as well as by services which are usually started automatically your operating system. Note: A system resource is sometimes called hardware resource, computer resource, or just resource.[2]
Resources which needs to be managed[edit]
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary memory | Primary Storage is the area in the computer where data is stored for quick access by the computer's processor. RAM is often synonymous with this term. |
| Secondary storage | Secondary storage is storage that is non-volatile, meaning that the data is kept even when the device is turned off. The data within a secondary storage device is also held until deleted or overwritten. Examples of secondary storage devices are: Hard Drives (HDD), Solid-State Drive (SSD), Floppy Disks and USB Drives. |
| processor speed | Measures in MHz (megahertz) and GHz (gigahertz), this is the number of instructions per second that the computer can execute. The CPU asks the OS for specific tasks using a bootloader (a bootloader is a computer program that loads the operating system when the computer powers on) |
| bandwidth | Bandwidth, which is the amount of data that can be transmitted in a fixed amount of time, is expressed in multiples of bits per second in digital devices. In analog devices, it is expressed in hertz. A "bus" with low bandwidth can hamper a fast hard drive. The operating system allocates bandwidth to each program, input or output method. |
| screen resolution | Number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It is usually quoted as width × height for example, "1024 × 768." The Screen resolution depends on the operating system (OS), as such one can change the screen resolution through the OS. |
| disk storage | Disk storage is a storage mechanism where data is recorded using various methods : Electronic, magnetic, optic or mechanical. Disk storage is stored by a computer processor and communicates within a computer with the use of input and output operations (I/O). Disk storage is managed by the operating system by determining when to read and write from a storage point. |
| sound processor | foo |
| graphics processor | foo |
| cache | Cache memory is a small-sized type of volatile computer memory that provides high-speed data access to a processor and stores frequently used computer programs, applications and data. It is the fastest memory in a computer, and is typically integrated onto the motherboard and directly embedded in the processor or main random access memory (RAM). |
| Network connectivity | foo |
Tools you can use to manage different parts of the Linux operating system[edit]
| The OS manages | Linux tools you can use to understand what is going on |
|---|---|
| Memory | top, htop, free, vmstat |
| Processes | top |
| Files | File system, df, du, mount, lsof |
| Security | fstab, last, who, /var/log/auth.log |
| CPU Scheduling | perf |
| Devices, Device I/O | iotop, iostat |
| Interrupts | perf |
| Networks | netstat, top, tcpdump, iptraf, iftop, nmon |
an excellent video to get you started[edit]
an image to help you see this in context[edit]
Standards[edit]
- Identify the resources that need to be managed within a computer system.
- Evaluate the resources available in a variety of computer systems.