Merkle tree: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
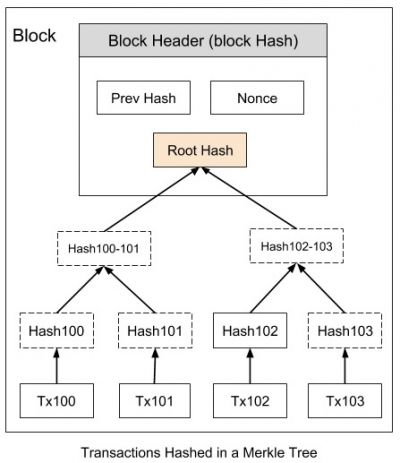
In cryptography and computer science, a hash tree or Merkle tree is a tree in which every leaf node is labelled with the cryptographic hash of a data block, and every non-leaf node is labelled with the hash of the labels of its child nodes. Hash trees allow efficient and secure verification of the contents of large data structures. Hash trees are a generalization of hash lists and hash chains.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merkle_tree</ref> | In cryptography and computer science, a hash tree or Merkle tree is a tree in which every leaf node is labelled with the cryptographic hash of a data block, and every non-leaf node is labelled with the hash of the labels of its child nodes. Hash trees allow efficient and secure verification of the contents of large data structures. Hash trees are a generalization of hash lists and hash chains.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merkle_tree</ref> | ||
[[File:Merkle tree.jpg| | [[File:Merkle tree.jpg|400px]] | ||
== Video == | |||
<html> | |||
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/s0fruNfgW30" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe> | |||
</html> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 18:19, 8 March 2020
Programming[1]
In cryptography and computer science, a hash tree or Merkle tree is a tree in which every leaf node is labelled with the cryptographic hash of a data block, and every non-leaf node is labelled with the hash of the labels of its child nodes. Hash trees allow efficient and secure verification of the contents of large data structures. Hash trees are a generalization of hash lists and hash chains.[2]
Video