Transmission medium: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Transmission media include: | Transmission media include: | ||
* metal conductor | * metal conductor (typically copper - about 300 Megabits per second (Mbps)) | ||
* fibre optic | * fibre optic (industrial glass - 940 Megabits per second (Mbps)) | ||
* wireless | * wireless (wireless - 150 Megabits per second (Mbps)) | ||
[[File:TransmissionMedium short.ogg]] | [[File:TransmissionMedium short.ogg]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:29, 29 November 2022
Networks[1]
The characteristics of different transmission media include:
- speed
- reliability
- cost
- security
Transmission media include:
- metal conductor (typically copper - about 300 Megabits per second (Mbps))
- fibre optic (industrial glass - 940 Megabits per second (Mbps))
- wireless (wireless - 150 Megabits per second (Mbps))
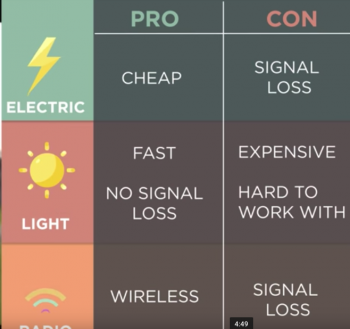
An image to learn about pro's and cons about different network media[edit]
I used this image (a screengrab) from a youtube video by the folks at code.org. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZhEf7e4kopM[2]
A good video, which touches more on transmission media and wireless[edit]
Some of the videos I show you don't exactly apply to our learning. This video is EXCELLENT and you should watch it many times.
See Also[edit]
Standards[edit]
These standards are used from the IB Computer Science Subject Guide[3]
- Outline the characteristics of different transmission media.
References[edit]
- ↑ http://www.flaticon.com/
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZhEf7e4kopM
- ↑ IB Diploma Programme Computer science guide (first examinations 2014). Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom: International Baccalaureate Organization. January 2012.