Linked list: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[file:arrows.png|right|frame|Programming basics<ref>http://www.flaticon.com/</ref>]] | [[file:arrows.png|right|frame|Programming basics<ref>http://www.flaticon.com/</ref>]] | ||
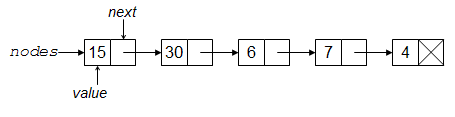
A linked list is a linear collection of data elements called nodes each pointing to the next node by means of a pointer. It is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of data and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing efficient insertion or removal from arbitrary element references <ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list</ref>. | |||
[[File:DataStructuresLinkedList.png]] | |||
Students should be able to sketch diagrams illustrating: adding a data item to linked list, deleting specified data item, modifying the data held | |||
in the linked list, searching for a given data item. | |||
== Singly linked list == | |||
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements, in which linear order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of data and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing efficient insertion or removal from arbitrary element references.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list#Singly_linked_list</ref> | |||
<br /> | |||
[[File:Singly-linked-list.png]] | |||
This video discusses the C programming language, but the content is clear to describe linked list. | |||
<html> | <html> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 23: | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
== | == Doubly linked lists == | ||
A doubly linked list is a linked data structure that consists of a set of sequentially linked records called nodes. Each node contains two fields, called links, that are references to the previous and to the next node in the sequence of nodes.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list</ref> | |||
<br /> | |||
<br /> | |||
[[File:Doubly-linked-list.png]] | |||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list Please reference this article for explanation of a doubly-linked list] | |||
This video discusses the C programming language, but the content is clear to describe linked list. | |||
<html> | <html> | ||
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/HmAEzp1taIE" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe> | <iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/HmAEzp1taIE" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
== Circularly linked list == | |||
In the last node of a list, the link field often contains a null reference, a special value used to indicate the lack of further nodes. A less common convention is to make it point to the first node of the list; in that case the list is said to be 'circular' or 'circularly linked'; otherwise it is said to be 'open' or 'linear'.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list#Circular_linked_list</ref> | |||
<br /> | |||
[[File:Circularly-linked-list.png]] | |||
<br /> | |||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list#Circular_Linked_list Please reference this article for more information about a circularly linked list] | |||
== Standards == | == Standards == | ||
| Line 47: | Line 53: | ||
* Sketch linked lists (single, double and circular). | * Sketch linked lists (single, double and circular). | ||
== | == External Links == | ||
* [[ | * [http://www.algolist.net/Data_structures/Singly-linked_list A good site with helpful information about linked lists] | ||
* [https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/StackLL.html An excellent site with an interactive animation about linked lists] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 10:53, 20 June 2019

A linked list is a linear collection of data elements called nodes each pointing to the next node by means of a pointer. It is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of data and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing efficient insertion or removal from arbitrary element references [2].
Students should be able to sketch diagrams illustrating: adding a data item to linked list, deleting specified data item, modifying the data held in the linked list, searching for a given data item.
Singly linked list[edit]
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements, in which linear order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of data and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing efficient insertion or removal from arbitrary element references.[3]
![]()
This video discusses the C programming language, but the content is clear to describe linked list.
Doubly linked lists[edit]
A doubly linked list is a linked data structure that consists of a set of sequentially linked records called nodes. Each node contains two fields, called links, that are references to the previous and to the next node in the sequence of nodes.[4]
![]()
Please reference this article for explanation of a doubly-linked list
This video discusses the C programming language, but the content is clear to describe linked list.
Circularly linked list[edit]
In the last node of a list, the link field often contains a null reference, a special value used to indicate the lack of further nodes. A less common convention is to make it point to the first node of the list; in that case the list is said to be 'circular' or 'circularly linked'; otherwise it is said to be 'open' or 'linear'.[5]
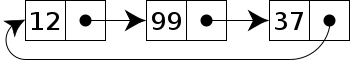
Please reference this article for more information about a circularly linked list
Standards[edit]
- Describe how linked lists operate logically.
- Sketch linked lists (single, double and circular).
External Links[edit]
- A good site with helpful information about linked lists
- An excellent site with an interactive animation about linked lists