Operating system: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| Processes || top | | Processes || top | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Files || File system | | Files || File system, df, du, mount | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Security || fstab | | Security || fstab | ||
|- | |- | ||
| CPU Scheduling | | CPU Scheduling || perf | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Devices, Device I/O | | Devices, Device I/O|| iotop, | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Interrupts | | Interrupts | ||
Revision as of 14:59, 1 September 2016
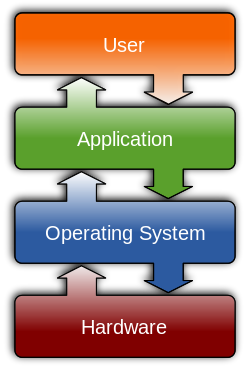
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. All computer programs, excluding firmware, require an operating system to function.[1]
An operating system manages:
| The OS manages | Linux tools you can use to understand what is going on |
|---|---|
| Memory | top, htop, free |
| Processes | top |
| Files | File system, df, du, mount |
| Security | fstab |
| CPU Scheduling | perf |
| Devices, Device I/O | iotop, |
| Interrupts | |
| The user interface, most often a GUI but also a CLI |
An operating system also provides:
- Tools for managing the operating system. These are often called utilities or system tools. Click here for a brilliant graphic showing the different types of tools you can use to view inside the Linux operating system
Different operating systems[edit]
- Linux
- OS X
- WIndows
- iOS
- Android OS
- Google chrome OS (Based on Linux)
Do you understand this topic?[edit]
- Describe the main functions of an operating system.
Do you have an advanced understanding about this topic?[edit]
- Describe how an operating system manages the functions you have just described above.