Distributed systems: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
* Shared load | * Shared load | ||
* Response more specific to environment | * Response more specific to environment | ||
Disadvantages of distributed system: | |||
* More complex to administrate | |||
* Less control | |||
Disadvantages of central systems: | |||
* Slower access | |||
* Computing load is on (usually) one device. | |||
* Response to a less specific environment | |||
== Standards == | == Standards == | ||
Revision as of 12:21, 8 October 2017
From John Rayworth's excellent site (here):
Centrally controlled system - A hardware and/or software IT system in which all parts of it are controlled by a central controller/server/mainframe[2].
(Purely) Distributed system - A hardware and/or software IT system in which various parts of the control and/or processing are controlled by individual controllers/servers/computers throughout the system[3].
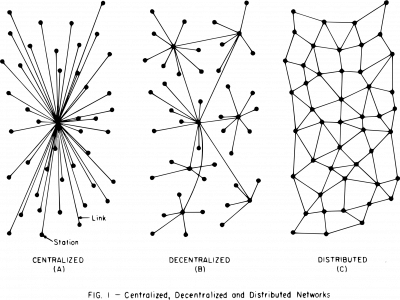
An important distinction[edit]
Please remember, for the rest of your life, the image below, and the distinction between centralized, decentralized, and distributed networks. Although we are learning about control, this idea is used in many different areas of computer science. Image used from https://openclipart.org/detail/277506/Centralized-Decentralized-and-Distributed-Networks who have released this under the Creative Commons Zero 1.0 License
Advantages of different systems[edit]
From the Dartford School[4]:
Advantages of central system:
- Easier to administrate
- More control
Advantages of distributed systems:
- Quicker access
- Shared load
- Response more specific to environment
Disadvantages of distributed system:
- More complex to administrate
- Less control
Disadvantages of central systems:
- Slower access
- Computing load is on (usually) one device.
- Response to a less specific environment
Standards[edit]
- Compare a centrally controlled system with a distributed system