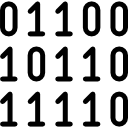Binary: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) (→Binary) |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
* '''binary''': A number expressed in the binary numeral system which represents numeric values using two different symbols: typically 0 (zero) and 1 (one).<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_number</ref> | * '''binary''': A number expressed in the binary numeral system which represents numeric values using two different symbols: typically 0 (zero) and 1 (one).<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_number</ref> | ||
* '''denary/decimal''': The decimal numeral system (also called base 10 or occasionally denary) has ten as its base.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decimal</ref> | * '''denary/decimal''': The decimal numeral system (also called base 10 or occasionally denary) has ten as its base.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decimal</ref> | ||
* '''hexadecimal''': In mathematics and computing, hexadecimal (also base 16, or hex) is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hexadecimal</ref> | * '''hexadecimal''': In mathematics and computing, hexadecimal (also base 16, or hex) is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hexadecimal</ref>. [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nrFHGtGdOzA Click here for an excellent video about hexidecimal] | ||
== Binary translation table == | == Binary translation table == | ||
Revision as of 07:15, 24 August 2016
This is an important concept. You should fully understand this.
In mathematics and digital electronics, a binary number is a number expressed in the binary numeral system or base-2 numeral system which represents numeric values using two different symbols: typically 0 (zero) and 1 (one). The base-2 system is a positional notation with a radix of 2. Because of its straightforward implementation in digital electronic circuitry using logic gates, the binary system is used internally by almost all modern computers and computer-based devices. Each digit is referred to as a bit.[1]
Binary[edit]
This is one of the better videos I've seen on binary. Content gratefully used with permission : [2]
Basic Definitions[edit]
- bit: A binary digit, either a 0 or 1.
- byte: A group of 8 adjacent binary digits (8 bits), on which a computer operates as a unit
- binary: A number expressed in the binary numeral system which represents numeric values using two different symbols: typically 0 (zero) and 1 (one).[3]
- denary/decimal: The decimal numeral system (also called base 10 or occasionally denary) has ten as its base.[4]
- hexadecimal: In mathematics and computing, hexadecimal (also base 16, or hex) is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16[5]. Click here for an excellent video about hexidecimal
Binary translation table[edit]
I find it helpful to draw this table when I must convert binary to base 10. It also helps when looking at the video above.
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
How to add two binary numbers[edit]
Adding binary is straight forward. Line up the numbers as you would if you were adding base-10 numbers.
Remember this:
0 + 0 = 0
0 + 1 = 1
1 + 0 = 1
1 + 1 = 10, so write a 0 and carry the 1 to the next column.
What you must know[edit]
You must be able to correctly answer the following questions:
- Define the term: bit
- Define the term: byte
- Define the term: binary
- Define the term: denary/decimal (they refer to the same thing)
- Define the term: hexadecimal
Why is this so important?[edit]
If we can represent numbers as 1 and 0, why not represent numbers as on and off? If we can represent letters as numbers (A = 65, B = 66) couldn't we also say A = 01000001 and B = 01000010? We can follow this line of thinking and make north / south, up / down, and low / high. Simple constructions that we can use to represent more complex numbers and even letters.
Binary representation is the essence of how computers work.
Resources[edit]
Click here for a slide deck that covers this topic nicely