DNS: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical decentralized naming system for computers, services, or other resources connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities. Most prominently, it translates more readily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying network protocols. By providing a worldwide, distributed directory service, the Domain Name System is an essential component of the functionality of the Internet, that has been in use since 1985.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain_Name_System</ref> | The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical decentralized naming system for computers, services, or other resources connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities. Most prominently, it translates more readily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying network protocols. By providing a worldwide, distributed directory service, the Domain Name System is an essential component of the functionality of the Internet, that has been in use since 1985.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain_Name_System</ref> | ||
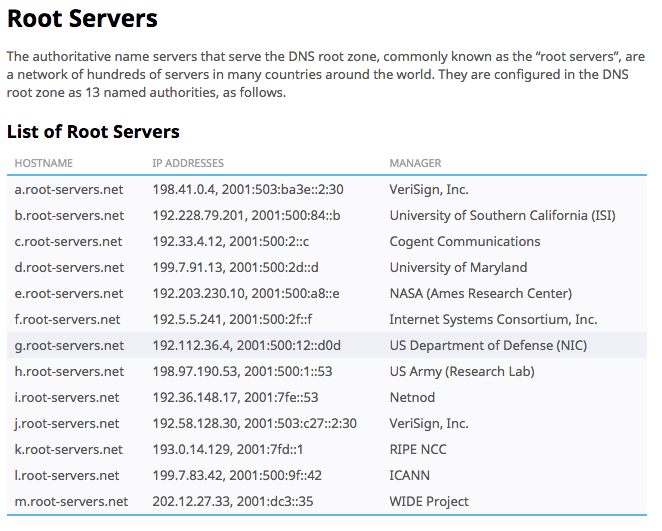
== Root servers == | |||
[[File:Dns root servers.png]] | |||
== Do I understand this? == | == Do I understand this? == | ||
Revision as of 14:24, 12 March 2017
DNS, the Domain Name System, is responsible for translating URLs of websites to IP addresses and vice versa. We need both IP addresses to be able to form a successful connection from sender to receiver.[2]
Introduction[edit]
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical decentralized naming system for computers, services, or other resources connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities. Most prominently, it translates more readily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying network protocols. By providing a worldwide, distributed directory service, the Domain Name System is an essential component of the functionality of the Internet, that has been in use since 1985.[3]
Root servers[edit]
Do I understand this?[edit]
This question is used from CS50[4]
- Why do we need (or rather, why is it nice to have) DNS?
Standards[edit]
These standards are used from the IB Computer Science Subject Guide[5]
- Describe how a domain name server functions.
References[edit]
- ↑ http://www.flaticon.com/
- ↑ http://cs50.wiki/DNS+and+DHCP
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain_Name_System
- ↑ http://cs50.wiki/DNS+and+DHCP
- ↑ IB Diploma Programme Computer science guide (first examinations 2014). Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom: International Baccalaureate Organization. January 2012.