How to ask for help: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| I can’t describe how to get a solution || [[#Algorithmic thinking; problem decomposition]] | | I can’t describe how to get a solution || [[#Algorithmic thinking; problem decomposition]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| I don’t know all the details || Real world problems require research | | I don’t know all the details || [[#Real world problems require research]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| I can solve it by hand, but I don’t know how to code it. || New Language Features | | I can solve it by hand, but I don’t know how to code it. || New Language Features | ||
Revision as of 12:53, 12 July 2017
Having problems is normal. If you do not learn how to solve your own problems, life will be difficult for you.
Step One: Why can't you write this program?[edit]
When you first realize you have a problem, follow these steps:
With gratitude to and permission from Stephen Hughes (Coe College) and Philip East (University of Northern Iowa)[1]
| Type of problem | What you need to do to solve it |
|---|---|
| I don't understand the problem | #Requirements Gathering |
| I can’t describe how to get a solution | #Algorithmic thinking; problem decomposition |
| I don’t know all the details | #Real world problems require research |
| I can solve it by hand, but I don’t know how to code it. | New Language Features |
| I can do it | Explore efficiency or professionalism. |
Requirements Gathering[edit]
Do you understand EVERY. SINGLE. WORD. in the problem? In this case the student needs to: re-examine the problem statement identifying specific problem requirements; play with the problem—draw pictures of interaction, imagine inputs & outputs, ...; seek clarification from the originator of the problem, etc.[2]
Algorithmic thinking; problem decomposition[edit]
If you don't know how to get to a solution, break the problem down into smaller parts.
A common obstacle novice programmers face arises from difficulty with problem representation—making the problem more concrete in their minds. They are not familiar with thinking abstractly in terms of variables and operations on them. The action in this case is to specify the desired outcome and begin problem decomposition from that point. Produce questions that indicate intermediate outcomes desired or information needed. Identify data needed to produce the outcomes and where that data must come from; necessary manipulations of the data; tasks that may need to be repeated or occur depending on some aspect of the problem data; etc.[3]
- Create a diagram of the problem
- Draw a picture of the problem
- Explain the problem to a rubber duck (really)
- Forget about a computer; how would you solve this with a pencil and paper?
- Think out loud
- Explain the problem to a friend
Checklist for solving problems when coding in PHP[edit]
How to view our linux error log[edit]
I encourage students to open a new tab in their terminal window. The command below will create a running list of errors. To escape from the output, push the key combination control-C.
tail -f /var/log/php/error.log
Problem Solving Steps[edit]
- Repeat the problem, make the error happen again
- TRACE the problem (click here to learn more) - Insert a notification or breakpoint into your program
- Google the problem in general terms. For example:
python how to import a calendar - Re-read your code (sometimes, reading backwards helps you see little errors)
- Use your debugging tools
- Ask a friend
- Google the specific error message your program is raising
- Don't ask your teacher until you have a very specific question.
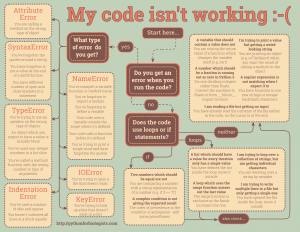
Click the image to learn about common mistakes[edit]
Other problem-solving strategies[edit]
- Walk away for a few minutes
- Take a short break (2 to 3 minutes)
- Physically stretch your body
- Explain the problem to a little rubber duck (really)