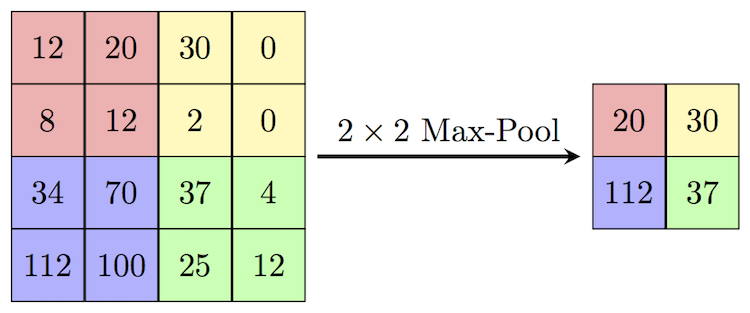Max-pooling / Pooling: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) (Created page with "<center> <blockquote style="padding: 5px; background-color: #FFF8DC; border: solid thin gray;"> File:Exclamation.png This is student work which has not yet been approve...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Please write a clear, concise description of your topic here.You will likely reference your introduction from somewhere else. Please use the following syntax at the end of each of your ideas. '''IT IS CRITICAL YOU ATTRIBUTE''' others work. Your introduction should be factual. No more than 3 or 4 sentences, please. Because you are not an expert in your topic, I expect you to triangulate your information. LOTS OF LINK TO OTHER RESOURCES PLEASE! | <!-- Please write a clear, concise description of your topic here.You will likely reference your introduction from somewhere else. Please use the following syntax at the end of each of your ideas. '''IT IS CRITICAL YOU ATTRIBUTE''' others work. Your introduction should be factual. No more than 3 or 4 sentences, please. Because you are not an expert in your topic, I expect you to triangulate your information. LOTS OF LINK TO OTHER RESOURCES PLEASE! | ||
<nowiki> | <nowiki> | ||
<ref> the url I cited by material from </ref> | <ref> the url I cited by material from </ref> | ||
</nowiki> | </nowiki> --> | ||
Max pooling is a '''sample-based discretization process'''. The objective is to down-sample an input representation (image, hidden-layer output matrix, etc.), reducing its dimensionality and allowing for assumptions to be made about features contained in the sub-regions binned.<ref>[https://www.quora.com/What-is-max-pooling-in-convolutional-neural-networks Link text], Jay Ricco, Quora.</ref> | |||
== How does it work | == How does it work and why== | ||
* If you are discussing a THING YOU CAN TOUCH, you must explain how it works, and the parts it is made of. Google around for an "exploded technical diagram" of your thing, [http://cdiok.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/MRI-Technology.jpg maybe like this example of an MRI] It is likely you will reference outside links. Please attribute your work. | <!-- * If you are discussing a THING YOU CAN TOUCH, you must explain how it works, and the parts it is made of. Google around for an "exploded technical diagram" of your thing, [http://cdiok.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/MRI-Technology.jpg maybe like this example of an MRI] It is likely you will reference outside links. Please attribute your work. | ||
* If you are discussing a PROCESS OR ABSTRACT CONCEPT (like [[fuzzy logic]]) you must deeply explain how it works. | * If you are discussing a PROCESS OR ABSTRACT CONCEPT (like [[fuzzy logic]]) you must deeply explain how it works. --> | ||
This is done to in part to help over-fitting by providing an abstracted form of the representation. As well, it reduces the computational cost by reducing the number of parameters to learn and provides basic translation invariance to the internal representation. | |||
Max pooling is done by applying a max filter to (usually) non-overlapping subregions of the initial representation. | |||
== Examples == | == Examples == | ||
Please include some example of how your concept is actually used. Your example must include WHERE it is used, and WHAT IS BENEFIT of it being used. | <!-- Please include some example of how your concept is actually used. Your example must include WHERE it is used, and WHAT IS BENEFIT of it being used. | ||
== Pictures, diagrams == | == Pictures, diagrams == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 32: | ||
# [https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Managing_files upload a file] | # [https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Managing_files upload a file] | ||
# [https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Images use the file on a wiki page] | # [https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Images use the file on a wiki page] --> | ||
Let's say we have a 4x4 matrix representing our initial input. | |||
Let's say, as well, that we have a 2x2 filter that we'll run over our input. We'll have a '''stride''' of 2 (meaning the (dx, dy) for stepping over our input will be (2, 2)) and won't overlap regions. | |||
For each of the regions represented by the filter, we will take the '''max''' of that region and create a new, output matrix where each element is the max of a region in the original input. | |||
Pictorial representation: | |||
[[File:MaxpoolSample2.png]] | |||
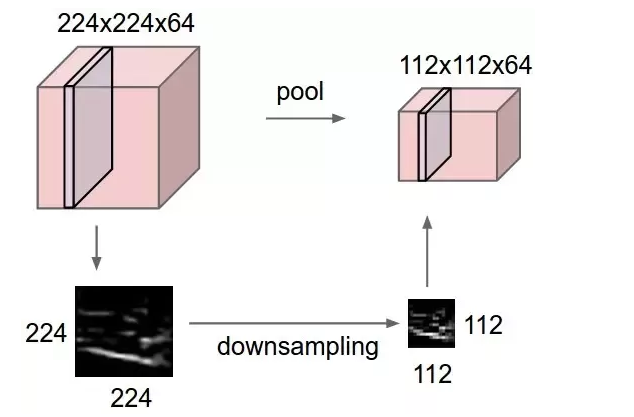
Real-life example: | |||
[[File:MaxpoolSample.png]] | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
Revision as of 21:15, 26 February 2018
This is student work which has not yet been approved as correct by the instructor

Introduction[edit]
Max pooling is a sample-based discretization process. The objective is to down-sample an input representation (image, hidden-layer output matrix, etc.), reducing its dimensionality and allowing for assumptions to be made about features contained in the sub-regions binned.[2]
How does it work and why[edit]
This is done to in part to help over-fitting by providing an abstracted form of the representation. As well, it reduces the computational cost by reducing the number of parameters to learn and provides basic translation invariance to the internal representation.
Max pooling is done by applying a max filter to (usually) non-overlapping subregions of the initial representation.
Examples[edit]
Let's say we have a 4x4 matrix representing our initial input. Let's say, as well, that we have a 2x2 filter that we'll run over our input. We'll have a stride of 2 (meaning the (dx, dy) for stepping over our input will be (2, 2)) and won't overlap regions.
For each of the regions represented by the filter, we will take the max of that region and create a new, output matrix where each element is the max of a region in the original input.
External links[edit]
- It would be helpful
- to include many links
- to other internet resources
- to help fellow students
- Please make sure the content is good
- and don't link to a google search results, please
References[edit]
- ↑ http://www.flaticon.com/
- ↑ Link text, Jay Ricco, Quora.