Operators
Operators are very important. The way the IB wants you to use operators is different than the way you will use them in real life.

An operator is something that takes one or more values (or expressions, in programming jargon) and yields another value (so that the construction itself becomes an expression)[2]
There are many different types of operators, but the ones we primarily concern ourselves with are boldfaced below:
- Operator Precedence
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Error Control Operators
- Execution Operators
- Incrementing/Decrementing Operators
- Logical Operators
- String Operators
- Array Operators
- Type Operators
An example of a simple array in PHP can be found below:
<?php
# this file is used to teach the VERY BASICS of arrays in PHP
$pizza_toppings = array (
"extra cheese"
"onions"
"pepperoni"
"ham"
"pineapple"
"chicken"
"arugula"
"pesto"
);
# This creates a very simple array with 8 items.
?>
A video[edit]
This video references the C programming language and scratch, but the ideas about operators are excellent. In the case of conditionals, PHP and C share similar syntax (but not exact).
The way the IB wants you to use operators[edit]
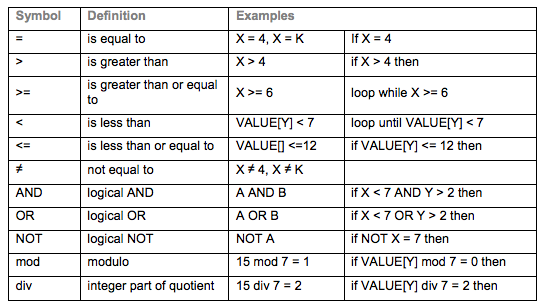
Please know all code submitted to the IB (with the exception of object oriented programming) is in pseudocode. The way we write operators in pseudocode is different than the way we might write them in the real world.
Below is a graphic that is taken from the above PDF file to help you understand how the IB wants operators to look.
Standards[edit]
- Define the terms: variable, constant, operator, object.
- Define common operators.
- Analyse the use of variables, constants and operators in algorithms.