Linked list

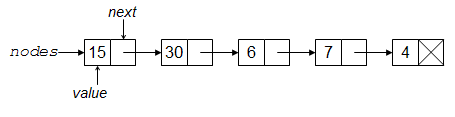
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements, called nodes, each pointing to the next node by means of a pointer. It is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of data and a reference (in other words, a link) to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing efficient insertion or removal from arbitrary element references [2].
In an array we are usually concerned about 2 things, the position (or the index) of an element and the element.
Students should be able to sketch diagrams illustrating: adding a data item to linked list, deleting specified data item, modifying the data held in the linked list, searching for a given data item.
singly linked list[edit]
This video discusses the C programming language, but the content is clear to describe linked list.
doubly linked lists[edit]
This video discusses the C programming language, but the content is clear to describe linked list.
Standards[edit]
- Describe how linked lists operate logically.
- Sketch linked lists (single, double and circular).
See Also[edit]
External Links[edit]
A good site with helpful information about linked lists
an excellent site with an interactive animation about linked lists