System calls

Resource Management[1]
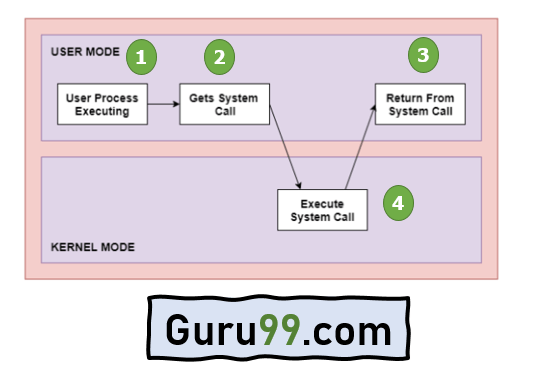
This diagram shows a simplified representation of a system call[2].
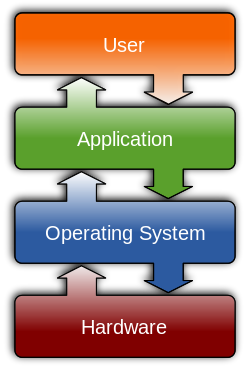
In computing, a system call (commonly abbreviated to syscall) is the programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service from the kernel of the operating system on which it is executed. This may include hardware-related services (for example, accessing a hard disk drive), creation and execution of new processes, and communication with integral kernel services such as process scheduling. System calls provide an essential interface between a process and the operating system.[3]
Categories of system calls can be grouped as noted below[4]:
- Process control
- create process (for example,
fork (operating system)|forkon Unix-like systems, orNtCreateProcessin the Windows NT, Native API) - Kill (command)|terminate process
- Loader (computing)|load, Exec (operating system)|execute
- get/set process attributes
- Wait (operating system)|wait for time, wait event, Signal (computing)|signal event
- Dynamic memory allocation|allocate and Garbage collection (computer science)|free memory
- create process (for example,
- File management
- create file, delete file
- open, close
- read, write, reposition
- get/set file attributes
- Device management
- request device, release device
- read, write, reposition
- get/set device attributes
- logically attach or detach devices
- Information maintenance
- get/set time or date
- get/set system data
- get/set process, file, or device attributes
- Communication
- create, delete communication connection
- send, receive messages
- transfer status information
- attach or detach remote devices
- Protection
- get/set file permissions