Design
Design is the creation of a plan or convention for the construction of an object, system or measurable human interaction (as in architectural blueprints, engineering drawings, business processes, circuit diagrams, and sewing patterns). Design has different connotations in different fields (see design disciplines below). In some cases, the direct construction of an object (as in pottery, engineering, management, coding, and graphic design) is also considered to be design.
Designing often necessitates considering the aesthetic, functional, economic, and sociopolitical dimensions of both the design object and design process. It may involve considerable research, thought, modeling, interactive adjustment, and re-design. Meanwhile, diverse kinds of objects may be designed, including clothing, graphical user interfaces, skyscrapers, corporate identities, business processes, and even methods of designing.
Thus "design" may be a substantive referring to a categorical abstraction of a created thing or things (the design of something), or a verb for the process of creation, as is made clear by grammatical context.[1]
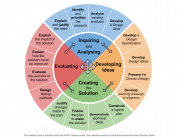
Big ideas in Design[edit]
Inquiring and Analyzing[edit]
- Explain and justify the need for a solution to a problem for a specified client/target audience
- Identify and prioritize the primary and secondary research needed to develop a solution to the problem
- Analyze a range of existing products that inspire a solution to the problem
- Develop a detailed design brief which summarizes the analysis of relevant research
Developing Ideas[edit]
- Develop a design specification which clearly states the success criteria for the design of a solution
- Develop a range of feasible design ideas which can be correctly interpreted by others
- Present the final chosen design and justify its selection
- Develop accurate and detailed planning drawings/diagrams and outline the requirements for the creation of the chosen solution
Creating the Solution[edit]
- Outline a plan, which considers the use of resources and time, sufficient for peers to be able to follow to create the solution
- Demonstrate excellent technical skills when making the solution
- Follow the plan to create the solution, which functions as intended
- List the changes made to the chosen design and plan when making the solution
- Present the solution as a whole
Evaluating[edit]
- Outline simple, relevant testing methods, which generate data, to measure the success of the solution
- Outline the success of the solution against the design specification
- Outline how the solution could be improved
- Outline the impact of the solution on the client/target audience
Standards[edit]
- Explain and justify the need for a solution to a problem for a specified client/target audience
- Identify and prioritize the primary and secondary research needed to develop a solution to the problem
- Analyse a range of existing products that inspire a solution to the problem
- Develop a detailed design brief which summarizes the analysis of relevant research
- Develop a design specification which clearly states the success criteria for the design of a solution
- Develop a range of feasible design ideas which can be correctly interpreted by others
- Present the final chosen design and justify its selection
- Develop accurate and detailed planning drawings/diagrams and outline the requirements for the creation of the chosen solution.
- Outline a plan, which considers the use of resources and time, sufficient for peers to be able to follow to create the solution
- Demonstrate excellent technical skills when making the solution
- Follow the plan to create the solution, which functions as intended
- List the changes made to the chosen design and plan when making the solution
- Present the solution as a whole
- Outline simple, relevant testing methods, which generate data, to measure the success of the solution
- Outline the success of the solution against the design specification
- Outline how the solution could be improved
- Outline the impact of the solution on the client/target audience
- Click here to see a test computer science students took about the design process
- design process
- What is a good design brief
- Click here for a copy of the MYP Design Guide
- Click here to see an EXCELLENT example of a design spec