Design
What is the web? How is the web made? This section delves into core components of the world-wide-web. If you are interested in building web applications, please visit that course page.
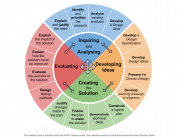
Big ideas in Design[edit]
Inquiring and Analyzing[edit]
- Explain and justify the need for a solution to a problem for a specified client/target audience
- Identify and prioritize the primary and secondary research needed to develop a solution to the problem
- Analyze a range of existing products that inspire a solution to the problem
- Develop a detailed design brief which summarizes the analysis of relevant research
Developing Ideas[edit]
- Develop a design specification which clearly states the success criteria for the design of a solution
- Develop a range of feasible design ideas which can be correctly interpreted by others
- Present the final chosen design and justify its selection
- Develop accurate and detailed planning drawings/diagrams and outline the requirements for the creation of the chosen solution.
Creating the Solution[edit]
- Outline a plan, which considers the use of resources and time, sufficient for peers to be able to follow to create the solution
- Demonstrate excellent technical skills when making the solution
- Follow the plan to create the solution, which functions as intended
- List the changes made to the chosen design and plan when making the solution
- Present the solution as a whole
Evaluating[edit]
- Outline simple, relevant testing methods, which generate data, to measure the success of the solution
- Outline the success of the solution against the design specification
- Outline how the solution could be improved
- Outline the impact of the solution on the client/target audience
Standards[edit]
|Explain and justify the need for a solution to a problem for a specified client/target audience|| Design |- |Identify and prioritize the primary and secondary research needed to develop a solution to the problem|| Design |- |Analyse a range of existing products that inspire a solution to the problem|| Design |- |Develop a detailed design brief which summarizes the analysis of relevant research|| Design |- style="background-color:#E6F9E6;" | colspan="2" | Developing Ideas |- |Develop a design specification which clearly states the success criteria for the design of a solution|| Design |- |Develop a range of feasible design ideas which can be correctly interpreted by others|| Design |- |Present the final chosen design and justify its selection|| Design |- |Develop accurate and detailed planning drawings/diagrams and outline the requirements for the creation of the chosen solution.|| Design |- style="background-color:#E6F9E6;" | colspan="2" | Creating the Solution |- |Outline a plan, which considers the use of resources and time, sufficient for peers to be able to follow to create the solution|| Design |- |Demonstrate excellent technical skills when making the solution|| Design |- |Follow the plan to create the solution, which functions as intended|| Design |- |List the changes made to the chosen design and plan when making the solution|| Design |- |Present the solution as a whole|| Design |- style="background-color:#E6F9E6;" | colspan="2" | Evaluating |- |Outline simple, relevant testing methods, which generate data, to measure the success of the solution|| Design |- |Outline the success of the solution against the design specification|| Design |- |Outline how the solution could be improved|| Design |- |Outline the impact of the solution on the client/target audience|| Design |}