Decentralization of the web

Decentralization is the process of distributing or dispersing functions, powers, people or things away from a central location or authority[2]. The web today is accessed via ISP (Internet Service Provider). Once a government or corporation controls or monitors the ISP, you can control and monitor individual web traffic.
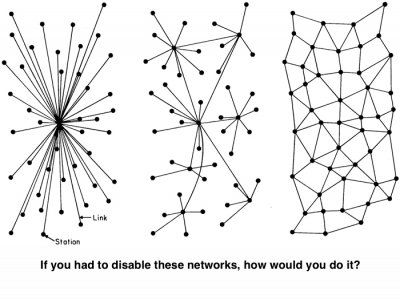
This topic looks at decentralized networks - with many different nodes - hosting and sharing content, so this there isn't
What is the decentralized web?[edit]
Although originally decentralized, nowadays the Web is suffering the surveillance of U.S. centralized control monopolies. The Decentralized Web is the global effort to re-decentralize the infrastructure, protocols, applications and governance of the Web.[3]
A Web designed to resist attempts to centralize its architecture, services, or protocols [so] that no individual, state, or corporation can substantially control its use. [4]
As there isn't one governing "overseer" of the web, and the web exists in the context of a Distributed networks, it is easy to imagine how the web can become more decentralized.
Do you understand this?[edit]
From the IB: Students should be aware of developments in mobile technology that have facilitated the growth of distributed networks.
Standards[edit]
These standards are used from the IB Computer Science Subject Guide[5]
- Explain why distributed systems may act as a catalyst to a greater decentralization of the web.
References[edit]
- ↑ http://www.flaticon.com/
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decentralization
- ↑ https://ischoolonline.syr.edu/blog/what-is-the-decentralized-web/
- ↑ https://ischoolonline.syr.edu/blog/what-is-the-decentralized-web/
- ↑ IB Diploma Programme Computer science guide (first examinations 2014). Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom: International Baccalaureate Organization. January 2012.