Binary tree: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
* They can be used to process the syntax of statements in natural and programming languages so are commonly used when compiling programming code. | * They can be used to process the syntax of statements in natural and programming languages so are commonly used when compiling programming code. | ||
== Tree - video example == | == Binary Tree - video example == | ||
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H5JubkIy_p8 This video provides a basic introduction to binary trees.] | ||
== Standards == | == Standards == | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 5 December 2016

Programming basics[1]
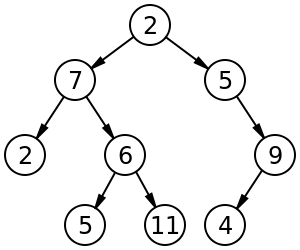
In computer science, a binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, which are referred to as the left child and the right child.[2]
Image of a tree[edit]
tree vocabulary[edit]
- root node
- parent node
- child node
- leaf node
Practical applications of a tree[edit]
- Trees can be used to store data that has an inherent hierarchical structure. For example, an operating system may use a tree for directories, files and folders in its file management system.
- They are dynamic, which means that it is easy to add and delete nodes.
- They are easy to search and sort using standard traversal algorithms.
- They can be used to process the syntax of statements in natural and programming languages so are commonly used when compiling programming code.
Binary Tree - video example[edit]
This video provides a basic introduction to binary trees.
Standards[edit]
- Describe how trees operate logically (both binary and non-binary).
- Define the terms: parent, left-child, right-child, subtree, root and leaf.
- State the result of inorder, postorder and preorder tree traversal.
- Sketch binary trees.
See Also[edit]
External Links[edit]
high level discussion of binary trees