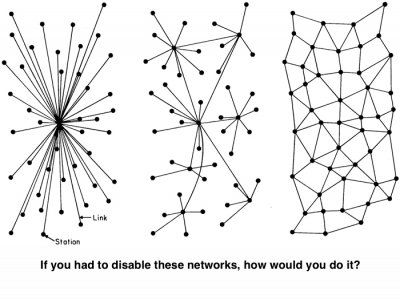
Decentralization of the web

Decentralization is the process of distributing or dispersing functions, powers, people or things away from a central location or authority[2]. The web today is accessed via ISP (Internet Service Provider). Once a hostile actor controls or monitors the ISP, they can control and monitor individual web traffic. Hostile actors also look at network chokepoints. Where does all network traffic converge to? This is another logical place to control and monitor.
What is the decentralized web?[edit]
Here are some excellent quotes from the school of information studies at Syracuse University related to decentralized web:
- Although originally decentralized, nowadays the Web is suffering the surveillance of U.S. centralized control monopolies. The Decentralized Web is the global effort to re-decentralize the infrastructure, protocols, applications and governance of the Web.[3]
- A Web designed to resist attempts to centralize its architecture, services, or protocols [so] that no individual, state, or corporation can substantially control its use. [4]
- A Decentralized Web belongs to all of us: Its power lies in our connections to each other. Its architecture encodes our values; its usage affirms our freedom to collaborate, share, and create.[5]
- A Decentralized Web is free of corporate or government overlords. It is to communication what local farming is to food. With it people can grow their own information.[6]
As there isn't one governing "overseer" of the web, and the web exists in the context of a Distributed networks, it is easy to imagine how the web can become more decentralized.
Do you understand this?[edit]
From the IB: Students should be aware of developments in mobile technology that have facilitated the growth of distributed networks.
Standards[edit]
These standards are used from the IB Computer Science Subject Guide[7]
- Explain why distributed systems may act as a catalyst to a greater decentralization of the web.
References[edit]
- ↑ http://www.flaticon.com/
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decentralization
- ↑ https://ischoolonline.syr.edu/blog/what-is-the-decentralized-web/
- ↑ https://ischoolonline.syr.edu/blog/what-is-the-decentralized-web/
- ↑ https://ischoolonline.syr.edu/blog/what-is-the-decentralized-web/
- ↑ https://ischoolonline.syr.edu/blog/what-is-the-decentralized-web/
- ↑ IB Diploma Programme Computer science guide (first examinations 2014). Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom: International Baccalaureate Organization. January 2012.