Functions
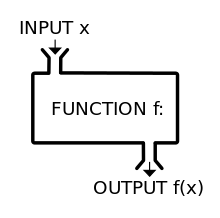
Introduction
We can control the flow of a program by calling a function. If we call a function, it executes, returns a value, and then resumes the program where it was called.
In programming, a named section of a program that performs a specific task is called a function. In this sense, a function is a type of procedure or routine. Some programming languages make a distinction between a function, which returns a value, and a procedure, which performs some operation but does not return a value.
Most programming languages come with a prewritten set of functions that are kept in a library. You can also write your own functions to perform specialized tasks. [2]
We use function so we don't need to repeat ourselves. Please watch the video below and remember the content.
The difference between returning and printing
Students often print from within a function. Please understand the difference between printing a result from a function and returning a result from a function.
print: gives the value to the user as an output string. print(3) would give a string '3' to the screen for the user to view. The program would lose the value.
return: gives the value to the program. Callers of the function then have the actual data and data type (bool, int, etc...) return 3 would have the value 3 put in place of where the function was called.[3]
In general, you should return a value from a function and not directly print from a function.
Example of a function
#
# this is a simple function that remembers who like hamburgers and who doesn't like hamburgers.
#
def likesHamburgers(name):
if name == "Alisher":
likes_hamburgers ="yes"
else:
likes_hamburgers="no"
return likes_hamburgers
print likesHamburgers("Bill")
print likesHamburgers("Alisher")
print likesHamburgers("foo")
Another classic example of a function
#
# this is a simple function
#
def calculator(number1, number2):
answer = number1 + number2
return answer
print calculator(12,43)
print calculator(91,673)
print calculator(1,3)
print calculator(87,1098)
Some decent videos about functions in Python