Hexadecimal
In mathematics and computing, hexadecimal (also base 16, or hex) is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16. It uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols 0–9 to represent values zero to nine, and A–F (or alternatively a–f) to represent values ten to fifteen.[1]
Basic Definitions[edit]
- bit: A binary digit, either a 0 or 1.
- byte: A group of 8 adjacent binary digits (8 bits), on which a computer operates as a unit
- binary: The binary numeral system is a base 2 number system.
- denary/decimal: The decimal numeral system (also called base 10 or occasionally denary) has ten as its base.[2]
- hexadecimal: In mathematics and computing, hexadecimal (also base 16, or hex) is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16[3]. Click here for an excellent video about hexidecimal
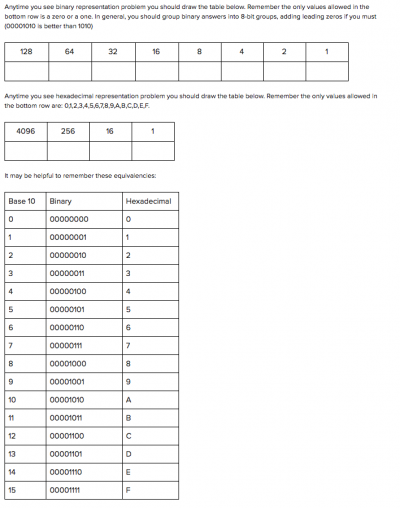
A helpful cheat sheet[edit]
What you must know[edit]
You must be able to correctly answer the following questions:
- Define the term: bit
- Define the term: byte
- Define the term: binary
- Define the term: denary/decimal (they refer to the same thing)
- Define the term: hexadecimal
Resources[edit]
Click here for a slide deck that covers this topic nicely