Interoperability and open standards

Interoperability[edit]
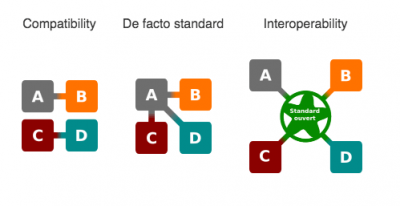
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system, whose interfaces are completely understood, to work with other products or systems, at present or future, in either implementation or access, without any restrictions.[2]
Interoperability describes the extent to which systems and devices can exchange data, and interpret that shared data. For two systems to be interoperable, they must be able to exchange data and subsequently present that data such that it can be understood by a user.[3]
Open standards[edit]
An open standard is a standard that is publicly available and has various rights to use associated with it, and may also have various properties of how it was designed (e.g. open process). There is no single definition and interpretations vary with usage.[4]
Do you understand this?[edit]
Standards[edit]
These standards are used from the IB Computer Science Subject Guide[5]
- Distinguish between interoperability and open standards.
References[edit]
- ↑ http://www.flaticon.com/
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interoperability
- ↑ http://www.himss.org/library/interoperability-standards/what-is-interoperability
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_standard
- ↑ IB Diploma Programme Computer science guide (first examinations 2014). Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom: International Baccalaureate Organization. January 2012.