Operating system: Difference between revisions
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) |
Mr. MacKenty (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Explain the role of an operating system == | == Explain the role of an operating system == | ||
An operating system (OS) is the most crucial software that runs on a computer, as it manages and controls the entire system's resources and activities. In terms of managing memory, peripherals, and hardware interfaces, the OS has several key responsibilities: | |||
=== Memory management === | |||
The OS is responsible for allocating and tracking memory usage by different programs and processes. This involves: | |||
a. Allocation: The OS divides memory into segments and allocates them to various applications and processes as needed. This ensures that each program has enough memory to execute properly. | |||
b. Protection: The OS ensures that one application or process cannot access another's memory space without proper authorization, thereby preventing data corruption or system crashes. | |||
c. Virtual memory: The OS can extend the available memory by creating a virtual memory space, which is a portion of the hard disk used as if it were physical memory (RAM). This enables the computer to run larger applications or processes even when the physical memory is limited. | |||
d. Paging and swapping: The OS can move data between RAM and secondary storage (e.g., hard disk) to optimize the use of available memory. Paging refers to the process of transferring fixed-sized memory blocks (pages) between RAM and the hard disk, while swapping refers to transferring entire processes. | |||
=== Peripheral management === | |||
The OS is responsible for managing peripheral devices (e.g., keyboards, mice, printers, and storage devices) by: | |||
a. Device drivers: The OS uses device drivers, which are software components that enable communication between the OS and peripheral devices. Drivers translate the OS's instructions into a language that the specific device can understand. | |||
b. Input/output (I/O) scheduling: The OS schedules and prioritizes I/O operations for various devices to ensure efficient data transfer and to avoid conflicts between devices. | |||
c. Buffering and caching: The OS uses buffers and caches to temporarily store data in memory during I/O operations. This allows the system to handle data transfers at varying speeds and minimizes the impact on performance. | |||
=== Hardware interface management === | |||
The OS is responsible for interfacing with the underlying hardware components (e.g., CPU, GPU, RAM, and storage devices) and ensuring that they work together smoothly. This involves: | |||
a. Processor management: The OS allocates CPU time to various processes and threads, ensuring that all applications receive an appropriate amount of computing resources. It also handles process scheduling, prioritization, and context switching. | |||
b. Interrupt handling: The OS manages hardware interrupts, which are signals generated by hardware devices (e.g., keyboard, mouse, or network card) to notify the OS of an event that requires immediate attention. The OS processes these interrupts and takes appropriate action, such as updating the display or saving data to disk. | |||
c. Power management: The OS optimizes the use of hardware resources to minimize power consumption, especially in battery-powered devices like laptops and smartphones. This involves techniques like adjusting CPU frequency, turning off unused devices, and managing sleep states. | |||
In summary, the operating system plays a crucial role in managing memory, peripherals, and hardware interfaces. By efficiently allocating resources, ensuring data protection, and providing a stable platform for applications to run, the OS enables a seamless user experience and optimal system performance. | |||
== Different operating systems == | == Different operating systems == | ||
| Line 30: | Line 43: | ||
# Linux | # Linux | ||
# OS X | # OS X | ||
# | # Windows | ||
# iOS | # iOS | ||
# Android OS | # Android OS | ||
# Google chrome OS (Based on Linux) | # Google chrome OS (Based on Linux) | ||
# Playstation OS (Orbis) | |||
# Blackberry | |||
# Nokia | |||
== A good video about operating systems == | == A good video about operating systems == | ||
| Line 56: | Line 72: | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
== | == Tools to view internal management of resources == | ||
An operating system also provides tools for managing the operating system. These are often called '''utilities''' or '''system tools'''. [[Media:Linux observability tools.png | Click here for a brilliant graphic showing the different types of tools you can use to view inside the Linux operating system]]. These tools give you insight and information for how the operating system is managing different resources. Below is a table with resources and tools to help you view how the OS is managing a particular resource. | An operating system also provides tools for managing the operating system. These are often called '''utilities''' or '''system tools'''. [[Media:Linux observability tools.png | Click here for a brilliant graphic showing the different types of tools you can use to view inside the Linux operating system]]. These tools give you insight and information for how the operating system is managing different resources. Below is a table with resources and tools to help you view how the OS is managing a particular resource. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 78: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! The OS manages !! Linux tools you can use || OS X tools you can use | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Memory || top, htop, free, vmstat || top, vm_stat, (gui) Activity monitor | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Processes || top || top, (gui) activity monitor | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Files || File system, df, du, mount, lsof || lsof, (gui) activity monitor, mount, df -h | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Security || fstab, last, who, /var/log/auth.log || last, who, (gui) console, ls -altr, groups | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | CPU Scheduling || perf || (gui) Activity monitor | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Devices, Device I/O|| iotop, iostat || (gui) activity monitor | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Interrupts || perf || ?? | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Networks || netstat, top, tcpdump, iptraf, iftop, nmon | | Networks || netstat, top, tcpdump, iptraf, iftop, nmon || netstat, lsof -i 4tcp | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Families of Operating system == | |||
Thank you to Alex M. for finding this image! | |||
[[File:Os family tree.png|900px]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:11, 21 March 2023
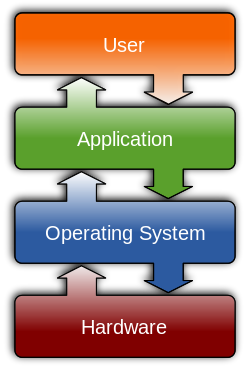
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. All computer programs, excluding firmware, require an operating system to function.[1]
Explain the role of an operating system[edit]
An operating system (OS) is the most crucial software that runs on a computer, as it manages and controls the entire system's resources and activities. In terms of managing memory, peripherals, and hardware interfaces, the OS has several key responsibilities:
Memory management[edit]
The OS is responsible for allocating and tracking memory usage by different programs and processes. This involves:
a. Allocation: The OS divides memory into segments and allocates them to various applications and processes as needed. This ensures that each program has enough memory to execute properly.
b. Protection: The OS ensures that one application or process cannot access another's memory space without proper authorization, thereby preventing data corruption or system crashes.
c. Virtual memory: The OS can extend the available memory by creating a virtual memory space, which is a portion of the hard disk used as if it were physical memory (RAM). This enables the computer to run larger applications or processes even when the physical memory is limited.
d. Paging and swapping: The OS can move data between RAM and secondary storage (e.g., hard disk) to optimize the use of available memory. Paging refers to the process of transferring fixed-sized memory blocks (pages) between RAM and the hard disk, while swapping refers to transferring entire processes.
Peripheral management[edit]
The OS is responsible for managing peripheral devices (e.g., keyboards, mice, printers, and storage devices) by:
a. Device drivers: The OS uses device drivers, which are software components that enable communication between the OS and peripheral devices. Drivers translate the OS's instructions into a language that the specific device can understand.
b. Input/output (I/O) scheduling: The OS schedules and prioritizes I/O operations for various devices to ensure efficient data transfer and to avoid conflicts between devices.
c. Buffering and caching: The OS uses buffers and caches to temporarily store data in memory during I/O operations. This allows the system to handle data transfers at varying speeds and minimizes the impact on performance.
Hardware interface management[edit]
The OS is responsible for interfacing with the underlying hardware components (e.g., CPU, GPU, RAM, and storage devices) and ensuring that they work together smoothly. This involves:
a. Processor management: The OS allocates CPU time to various processes and threads, ensuring that all applications receive an appropriate amount of computing resources. It also handles process scheduling, prioritization, and context switching.
b. Interrupt handling: The OS manages hardware interrupts, which are signals generated by hardware devices (e.g., keyboard, mouse, or network card) to notify the OS of an event that requires immediate attention. The OS processes these interrupts and takes appropriate action, such as updating the display or saving data to disk.
c. Power management: The OS optimizes the use of hardware resources to minimize power consumption, especially in battery-powered devices like laptops and smartphones. This involves techniques like adjusting CPU frequency, turning off unused devices, and managing sleep states.
In summary, the operating system plays a crucial role in managing memory, peripherals, and hardware interfaces. By efficiently allocating resources, ensuring data protection, and providing a stable platform for applications to run, the OS enables a seamless user experience and optimal system performance.
Different operating systems[edit]
- Linux
- OS X
- Windows
- iOS
- Android OS
- Google chrome OS (Based on Linux)
- Playstation OS (Orbis)
- Blackberry
- Nokia
A good video about operating systems[edit]
An excellent video about operating systems[edit]
Virtual memory[edit]
As we discuss the ways in which an operating system manages resources, we start to learn about virtual memory. A superb video can be found below to help you understand this:
Tools to view internal management of resources[edit]
An operating system also provides tools for managing the operating system. These are often called utilities or system tools. Click here for a brilliant graphic showing the different types of tools you can use to view inside the Linux operating system. These tools give you insight and information for how the operating system is managing different resources. Below is a table with resources and tools to help you view how the OS is managing a particular resource.
| The OS manages | Linux tools you can use | OS X tools you can use |
|---|---|---|
| Memory | top, htop, free, vmstat | top, vm_stat, (gui) Activity monitor |
| Processes | top | top, (gui) activity monitor |
| Files | File system, df, du, mount, lsof | lsof, (gui) activity monitor, mount, df -h |
| Security | fstab, last, who, /var/log/auth.log | last, who, (gui) console, ls -altr, groups |
| CPU Scheduling | perf | (gui) Activity monitor |
| Devices, Device I/O | iotop, iostat | (gui) activity monitor |
| Interrupts | perf | ?? |
| Networks | netstat, top, tcpdump, iptraf, iftop, nmon | netstat, lsof -i 4tcp |
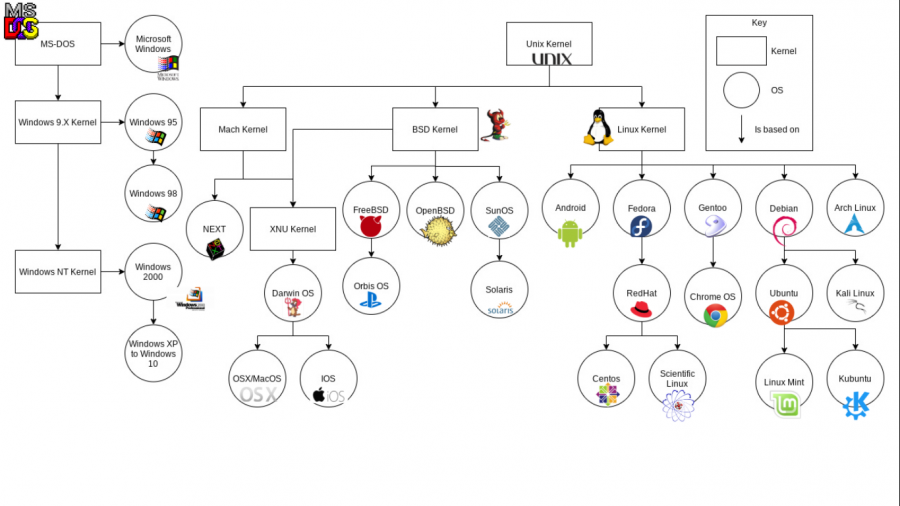
Families of Operating system[edit]
Thank you to Alex M. for finding this image!
Standards[edit]
- I can explain the role of the operating system in terms of managing memory, peripherals and hardware interfaces.